Sugars
- A carbohydrate is an organic compound composed of sugar molecules.
- Sugars contain carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen. Simple sugars containing just one single sugar unit are called monosaccharides
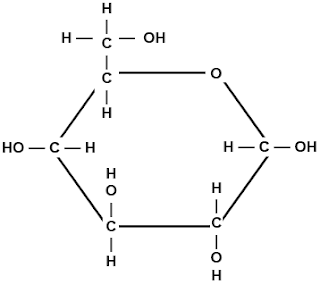
- An example of a monosaccharide, Gulcose, form in straight-chains and in ring-shaped forms.
- Disaccharides also known as "double sugar" construct from two monosaccharides.
- Polysaccharides are long chains made up of simple sugar monomers.
- Plants need energy to perform work.
- Animals and humans store sugar in form of a polysaccharide called glycogen.
- Cellulose work as a building material.
- Cullulose helps us keep our digestive system in our body healthy
Concept Check
1.)Explain the difference between a monosaccharide and a dissacharide. Give an example of each.
Monosaccharides are simple sugars that contain just one unit, for example, gluscose and galactose. Dissacharides are constructed by two monosaccharides, an example of this is sucrose.
2.)Compare and contrast starch, glycogen, and cellulose.
Starch, glycogen and cellulose are all glucose monomers. Glycogen is used as a storage for excess sugar in a animals body. In addition, cellulose is used in plants to help stiffen plants, and preventing it from falling. Starch acts as a source of energy for animals and humans, we need starch in order to perform work.
3.)How do animals store excess glucose molecules?
Animals store excess gluclose molecules in a glycogen;when our body needs energy, it breaks down the glycogen granules which causing it to releasing glucose.
No comments:
Post a Comment