1.) Wich of the followinf is NOT organic molecule?
C. Water
2.) Which of the following terms includes all the other terms on this list?
D. Polyssacharides
3.) Which term is most appropriate to describe a molecule that dissolves easily in water?
C. Hydrophilic
4.) Cholesterol is an example of what kind of molecule?
B. Lipids
5.) The 20 amino acids vary only in their...
C. Amino groups
6.) A specific reactant an enzme acts upon is called the ...
D. Substrate
7.) An enzyme does which of the following ?
B. Lowers the activation energy of a reaction
8.) Besides satisfying your hunger, why else might you consume a big bowl of pasta the night before a race?
I might consume a bowl of pasta because pasta provides me carbohydrates which i need to give me energy.
9.) How are glucose,sucrose and starch related?
They are related because they are all sugars, and they all contained in a plant. Sucrose is a major carbohydrate in a plant sap; starches are made up of glucose monomer that are found in plant cells.
10.) What are steriods? Describe 2 functions they have in cells.
Steriods are lipid molecules which contain carbon skeletons that forms four fused rings. The 2 different functions effect the appearance between male and female, estrogen for femals and testosterone for male.
11.) How are popypeptides related to proteins?
Proteins are made by the link of amino acids which makes a chain, this chain is called a polypeptide.
12.) How does denaturation affect the ability they have in cells?
Denaturation affect the ability they have in cells because once they unravel, it caused the cells to not function properly.
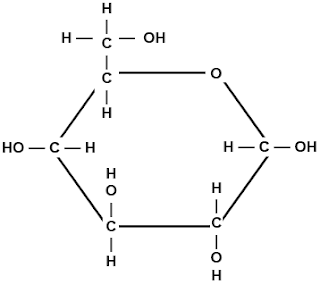
14a.) One product of this reation is represented by a question mark. Which molecule is it?
Hydrogen Molecule .
b.) What kind of reaction is this called? Explain
It is a Dehydration reaction because two hydrogen and oxygen molecules are released so that they can bond together.
c.) If an amino acid is added to this chain, at what two places could it attach?
I think it would be added at the OH and H.
15a.) At which temperature does enzyme A perfom best? Enzyme B?
Enzyme A: 37 celcius
Enzyme B: 77 celcius
b.) Knowing that one of these Enzymes is found in humans and other inthermophilic (heat-loving) bacteria, hypothesize which enzyme came from which organism.
I think that enzyme A is found in humans, since a normal temperature for a human would be about 37 celcius. And enzyme B could be found in baterica, due to its high temperature.
c.) Propose a hypothesis that explains why the rate of reaction catalyzed by a enzyme A slows down at temperatures above 40 celcius
In my opinion, i think enyme A slows down because it might be too hot for it to function properly, and therefore the rate of reaction decreases.